Scientific Explorations
Nasa moon caves – NASA’s exploration of lunar caves holds immense scientific significance, offering a unique opportunity to uncover hidden secrets of the moon. These caves, shielded from cosmic radiation and temperature fluctuations, present a potential haven for life and provide valuable insights into the moon’s geological history.
In the vast expanse of the lunar landscape, NASA’s unwavering quest for hidden moon caves continues, promising a glimpse into the Moon’s enigmatic past. These subterranean sanctuaries may hold valuable clues to the Moon’s origins and potential for future exploration.
While the search intensifies, renowned investor Bill Ackman ‘s vision of lunar mining adds a captivating layer to the endeavor. As we delve deeper into the Moon’s secrets, the tantalizing allure of moon caves remains a beacon of scientific discovery, beckoning us to unravel the mysteries that lie beneath the lunar surface.
Lunar caves have captured the scientific community’s attention due to their potential to harbor microbial life. The stable conditions within the caves, including protection from radiation and temperature extremes, create a suitable environment for life to thrive. Moreover, caves provide access to resources such as water ice, which could sustain life forms.
NASA’s moon caves, vast and enigmatic, have long captivated our imagination. They offer a glimpse into the Moon’s hidden past and potential future. However, their exploration has been hindered by the lack of a suitable vehicle. The recent development of the Artemis rover, inspired by J.D.
Vance’s wife , holds promise for unlocking these lunar mysteries, paving the way for scientific breakthroughs and human exploration.
Exploration Objectives, Nasa moon caves
- Search for evidence of past or present life, including fossils, organic molecules, or microbial communities.
- Investigate the geological processes that shaped the caves, providing insights into the moon’s history and evolution.
- Study the environmental conditions within the caves, including temperature, radiation levels, and the presence of water or other resources.
Scientific Instruments and Techniques
- Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS): Used to analyze the chemical composition of cave walls and search for organic molecules.
- Ground-penetrating radar: Used to map the structure and extent of caves, including hidden chambers and passages.
- Microbiological samplers: Used to collect samples of potential life forms from cave surfaces and environments.
Technological Advancements

NASA’s exploration of lunar caves relies heavily on cutting-edge technologies and equipment. These include:
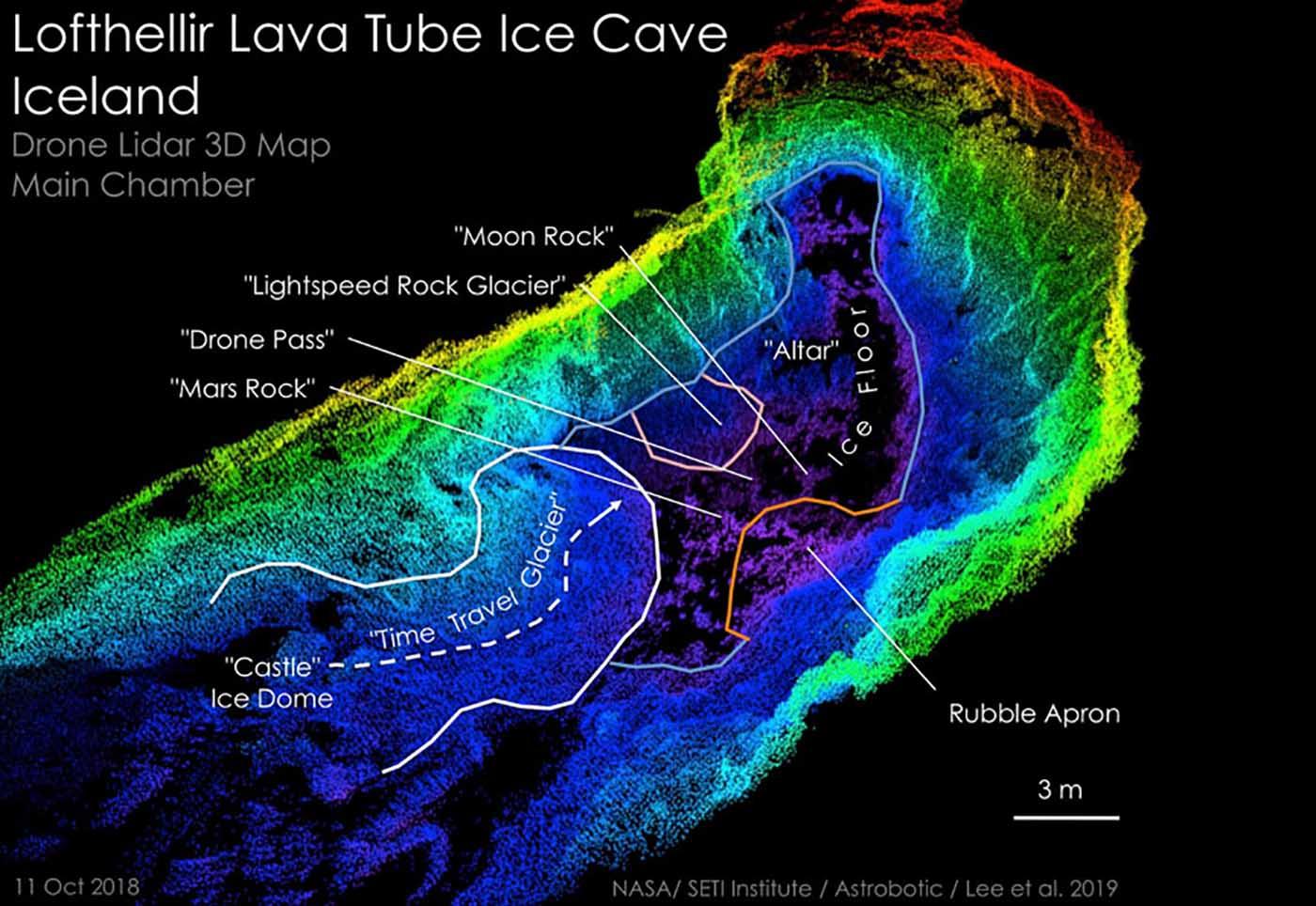
- Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to create detailed 3D maps of the caves’ interiors, enabling scientists to navigate and study them remotely.
- Rover-mounted cameras: Rovers equipped with high-resolution cameras provide real-time images of the caves, allowing scientists to assess their geological features and potential habitability.
- Laser scanning: This technique uses lasers to create precise cross-sections of the caves, revealing their structural details and any hidden passages.
- Drilling equipment: To collect samples from the cave walls and floors, scientists use specialized drilling equipment that can penetrate the lunar regolith.
- Autonomous navigation systems: To navigate the complex and potentially hazardous cave environments, rovers are equipped with autonomous navigation systems that allow them to avoid obstacles and map their surroundings.
Mapping Lunar Caves
Mapping lunar caves presents unique challenges. The extreme darkness, uneven terrain, and limited communication capabilities make it difficult to navigate and create accurate maps. To overcome these challenges, scientists have developed innovative solutions:
- Lidar-based mapping: Lidar technology is particularly valuable for mapping lunar caves because it can penetrate darkness and provide highly detailed 3D data.
- SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping): SLAM algorithms allow rovers to build maps of their surroundings while simultaneously determining their own location, improving navigation and mapping accuracy.
- Visual odometry: This technique uses cameras to estimate the rover’s motion and orientation, enabling it to create maps based on visual data.
- Data fusion: By combining data from multiple sensors, such as lidar, cameras, and inertial measurement units, scientists can create more comprehensive and accurate maps of lunar caves.
Future Missions and Implications: Nasa Moon Caves
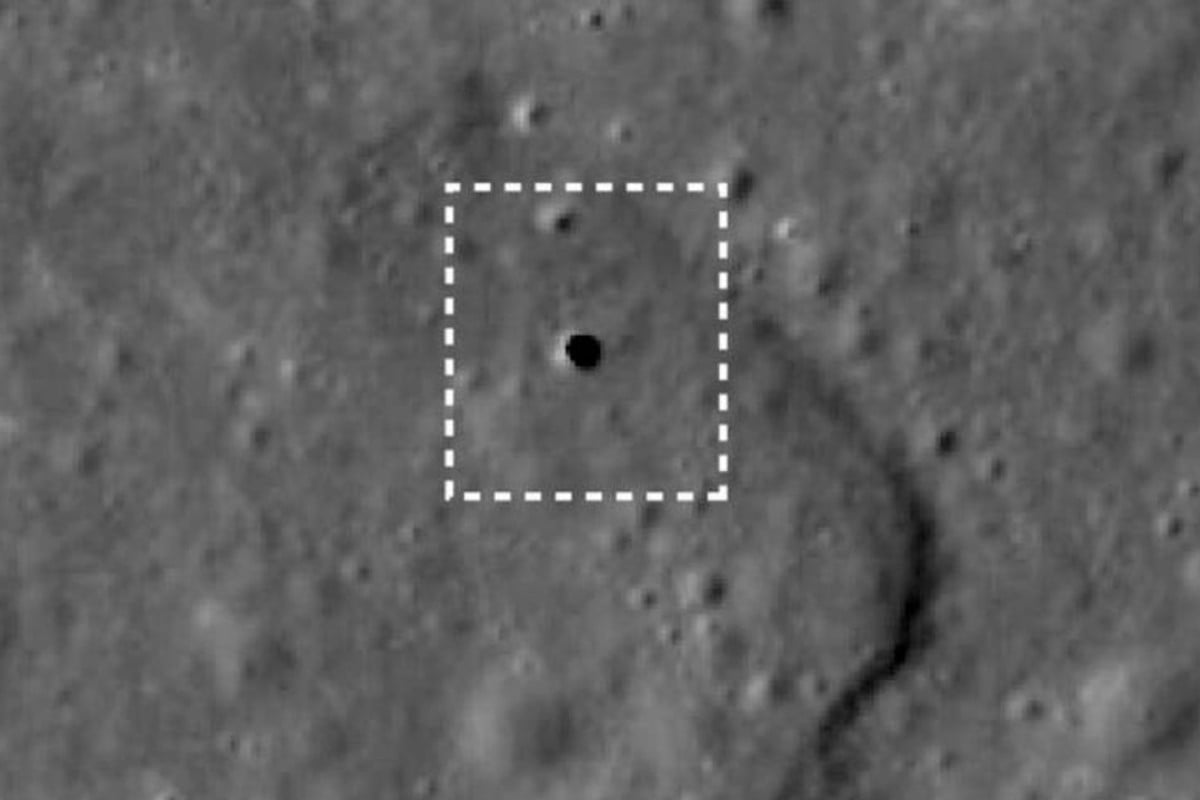

NASA’s plans for future missions to lunar caves hold immense potential for advancing our scientific understanding and technological capabilities. These missions aim to explore the vast and enigmatic caves found on the Moon, which are believed to hold valuable insights into the Moon’s geological history and the potential for sustaining human life in space.
One of the primary goals of future lunar cave missions is to establish a permanent lunar base. By utilizing the caves’ natural protection from radiation and extreme temperatures, a lunar base could provide a safe and sustainable habitat for astronauts conducting long-term scientific research and exploration. The base would serve as a hub for scientific experiments, resource extraction, and technological advancements, enabling humans to establish a permanent presence on the Moon.
Resource Extraction
Lunar caves also present opportunities for resource extraction, particularly of water ice and minerals. Water ice is a crucial resource for human life and can be used for drinking, generating oxygen, and producing rocket fuel. Minerals found in lunar caves, such as rare earth elements and helium-3, have valuable applications in various industries, including electronics, energy production, and medical research.